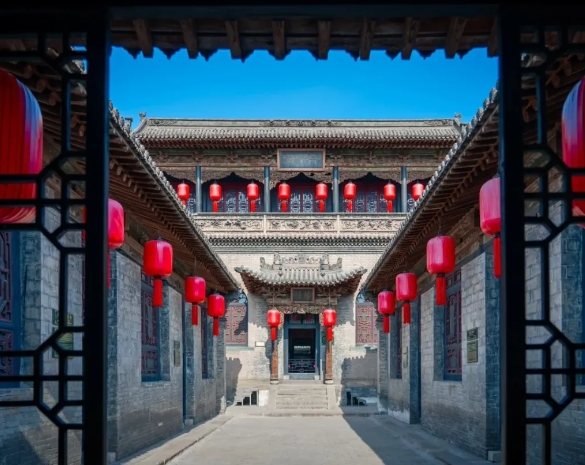
To the east of the Yellow River and to the west of the Taihang Mountains lies a land shaped by great mountains and rivers. In ancient times, it was called Hedong. Now it is called Shanxi. “Surrounded by rivers and mountains” is its exclusive synonym. (Surrounded by rivers and mountains means there are great rivers outside and high mountains inside, referring to natural barriers of mountains and rivers. It comes from “Zuo Zhuan”, and Shanxi is described as “surrounded by rivers and mountains”.)
The 716-kilometer Fen River flows grandly from north to south and runs through almost half of Shanxi’s territory. “Pointing to the Taihang Mountains with the left hand and Lvliang Mountains with the right hand.” The two majestic mountain ranges running from north to south stand in opposition on both sides of the Fen River, presenting a geographical pattern of “two mountains flanking a river”. And surrounding the two mountains and one river is the surging “Mother River” – the Yellow River. Shanxi is also known as “San Jin”. (San Jin originally referred to the combination of the states of Wei, Zhao, and Han during the Warring States Period. As a geographical term, it refers to the former Jin State where Wei, Zhao, and Han are located. Later, it evolved into another name for Shanxi Province.) It is one of the important birthplaces of the Chinese nation. It preserves the most complete memory of 5,000 years of Chinese civilization and is known as the “cradle of Chinese civilization”. It is often called “the museum of ancient Chinese culture”.
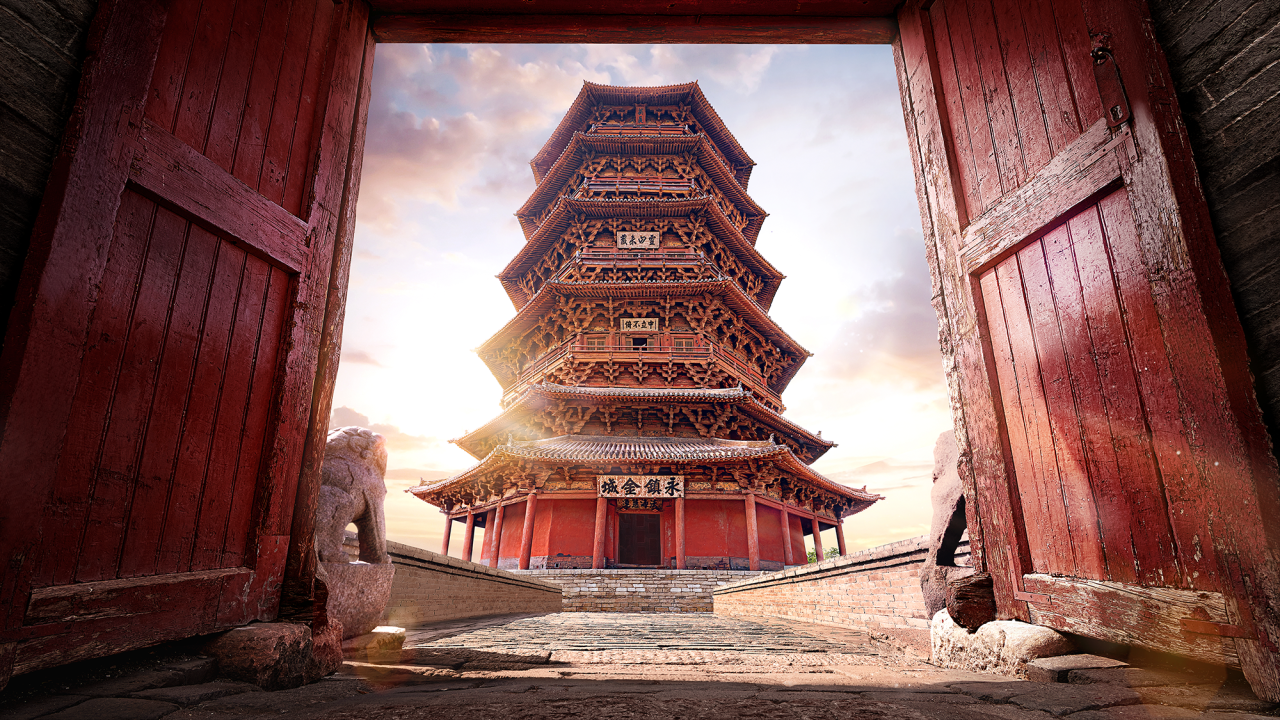
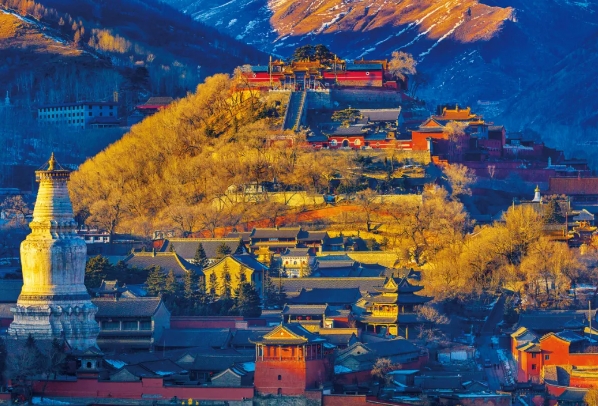
Open the cultural map. There is Mount Heng, one of the Five Great Mountains; Mount Wutai, one of the four major Buddhist holy lands; Yungang Grottoes, one of the four major Buddhist grottoes; Pingyao Ancient City, one of the four best-preserved ancient cities in China; and the Guandi Temple in Jiezhou, Yuncheng, the “ancestor of martial temples”; and the Hukou Waterfall, the “world’s largest yellow waterfall”…
Beautiful landscapes and rare ancient architectural remains are scattered and inlaid on the land of Shanxi.

▲ Hukou Waterfall.
The forest area of Shanxi is 2.824 million hectares. The forest coverage rate reaches 23.57%. There are densely distributed eight national-level nature reserves such as Lishan, Manghe River, Pangquangou, and Luya Mountain. Nine large forest areas such as Guancen Mountain, Taiyue Mountain, and Zhongtiao Mountain. Twenty-six national forest parks such as Mount Wutai, Tianlong Mountain, Guandi Mountain, and Wulaofeng. Eleven national geological parks such as Hukou Waterfall, Ningwu Perennial Ice Cave, and Datong Volcanic Cluster.
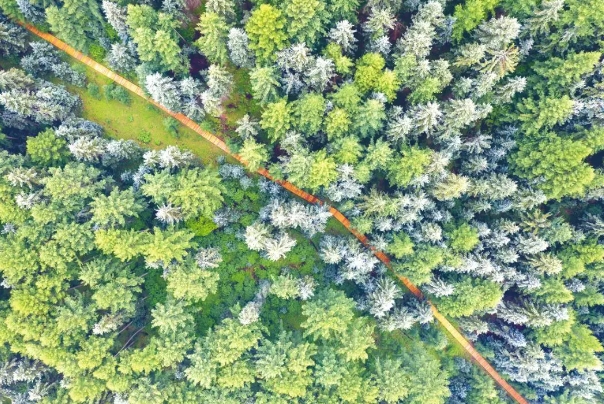

▲ Guancen Mountain National Forest Park.
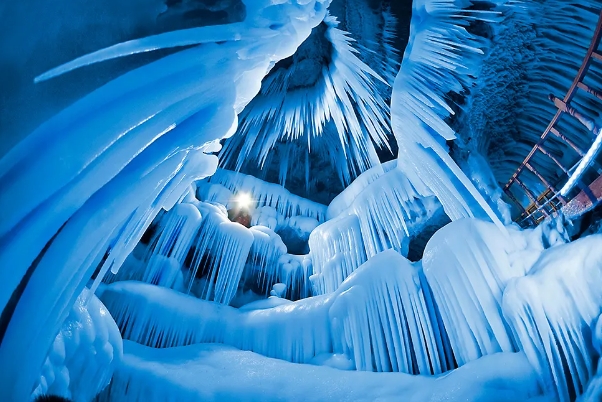

▲ Luya Mountain Perennial Ice Cave.

























